Eev and Maxima
- 1. eepitch-maxima
- 2. find-angg-es-links
- 3. Elisp hyperlinks
- 4. Embedding in LaTeX
- 5. "Physicist's notation"
- 6. Substitution
- 7. LispTree (and LuaTree)
- 8. Maxima by Example
- 9. Qdraw
- 10. Debugging the Lisp (with Sly)
- 11. Maxima for students
1. eepitch-maxima
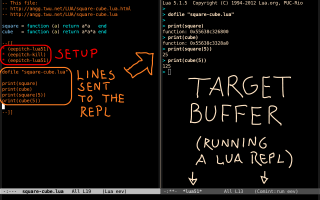
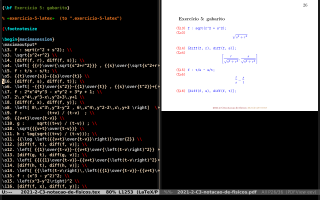
I use eepitch to send lines from Emacs to Maxima; see the figure below for the main idea, and my presentation at the EmacsConf2021 for the details. The definition of eepitch-maxima in eev is the simplest possible - just this:
(defun eepitch-maxima () (interactive) (eepitch-comint "maxima" "maxima"))
I tried to write variants that used Fermin MF's maxima-mode instead of just comint, but his maxima-mode behaved in weird ways when it had to send empty lines, and we couldn't fix that easily... so I gave up.
2. find-angg-es-links
The video below explains a way to run my executable notes on Maxima with eev without downloading anything extra. Click on the first screenshot to go to the page about that video, and click on the third screenshot to play the very nice demo that starts at 15:14... or actually to read the subtitles of that part; then click on the timemark to play the video.
Click on the second screenshot to play (or to read the subtitles of) the video starting from 11:30. That part has a very technical explanation of the "...without downloading anything extra" - not very recommended! 😕
3. Elisp hyperlinks
My notes on Maxima in maxima.e contain lots of elisp hyperlinks like these ones,
(find-maximanode "makelist") (find-maximamsg "37690886 202208 07" "RToy: doc/info/build-html-index.lisp") |
that are htmlized in special ways. They are explained in these other pages: find-maximanode, find-maximamsg.
4. Embedding in LaTeX
A newer update: see this page.
An older update: my current way of LaTeXing Maxima code uses Lpeg. Its main module is here, Maxima2.lua, and it produces output like this from this input (plus tweaking). The rest of this section describes an older way.
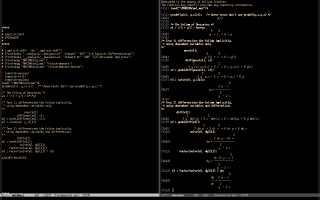
Here is an example of how I am embedding Maxima code in LaTeX files; the trick that makes eepitch ignore a prefix is explained here. If I execute that eepitch block skipping the lines "load" and "display2d" I get a human-friendly output, as in the first screenshot below; if I execute the lines "load" and "display2d" I get an output that I can process with M-x emaxima-conv (that calls emaxima.lua) to obtain this LaTeX code, that becomes this in the PDF. This trick is based on the answers that I got for this question that I sent to Maxima mailing list; note that 1) I am using this copy of emaxima.sty that has two lines commented out, and 2) my emaxima.lua is a quick hack, and it should be converted to elisp at some point.
5. "Physicist's notation"
First version: In 2022jan10 I sent to the Maxima mailing list this big e-mail, that had two parts. In the first part I asked about the (internal) differences between using expressions, like "f : x^2", and using functions, like "g(x) := x^3"; the code associated to that part is here. In the second part I asked if, and how, Maxima supports "physicists' notation" - where "physicists' notation" ("PN") is my informal name for a notation that is common in old books like this one by Silvanus Thompson. In PN variables and functions can share the same names, variables can be "dependent", some arguments can be omitted, and several abbreviations are standard - for example, if y=y(x) then the default meaning for y1 is y1=y(x1)=y(x0+Δx). It turns out that YES, Maxima supports physicists' notation, and it's easy to translate calculations in PN to Maxima if we use gradef and subst in the right way to translate between PN and "mathematician's notation". I recorded a 20s video demo-ing this - it's here, and its code is here. The slides on PN that I prepared for my course on Calculus 3 are here.
Second version (sep/2023): my sample space is small - about 25 people - but apparently in Brazil,
- "all" the "P"ure mathematicians ("group P") treat dependent variables and differentials as abuses of language,
- "all" the "A"pplied mathematicians, physicists and engineers ("group A") treat dependent variables and differentials as something that "everybody knows", and
- no one in either of the two groups knows the exact rules for translating the language of "Calculus with dependent variables and differentials" ("Calculus+") into the language of "Calculus without dependent variables and differentials" ("Calculus-")...
...so "no one" here knows how write an "elaborator", in this sense, that could translate "Calculus+" into "Calculus-". I grew up in Group A and my native language is "Calculus-", but now in my day job I'm teaching integration using books that use "Calculus+", and I thought that the best way to handle my embarassment for not speaking "Calculus+" well enough would be to formalize how that translation can be done.
I'm sort of working on that, and I'm starting by writing some of its functions in Maxima; my functions are here: pn1.mac. That file is a bare prototype at the moment, but to me it feels like the right way to treat dependent variables and differentials as abbreviations. Here is a screenshot:
6. Substitution
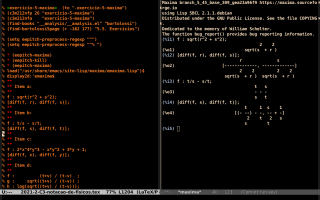
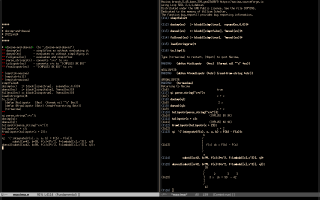
My first attempts to understand how Maxima implements the "#$expr$" syntax in Lisp are here: 1, 2, 3. Then Stavros Macrakis explained how I could define "dosimp" and "doeval" and I produced the example below. Its code is here. My long e-mail explaining why I am teaching substitution in this way is here (includes gossip).
7. LispTree (and LuaTree)
LispTree displays Maxima objects as trees. For example, if we run
* (eepitch-maxima) * (eepitch-kill) * (eepitch-maxima) load("~/lisptree/lisptree.mac") lisptree0_config('lisp)$ lisptree(fundef(format)); lisptree0_config('maxima)$ lisptree(fundef(format)); |
it shows the definition of format as a tree in two different styles:
|
|
Its page is here.
It supersedes LuaTree, that was a quick hack and was hard to install.
8. Maxima by Example
Update: See my page on (My)Qdraw.
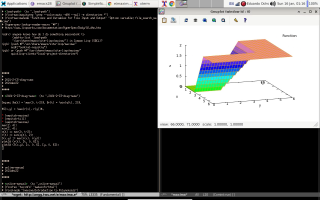
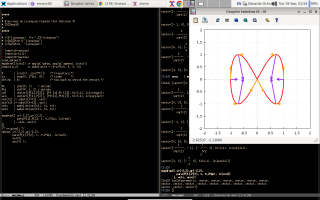
The best place for learning Maxima from examples is a (free) book whose name is - ta-daaa! - Maxima by Example. It is divided into chapters, and my script to download a local copy of it is here. Its chapter 13 is about qdraw, that is a front-end to Maxima's plot and draw commands. I find qdraw much easier to use than plot and draw; for example, the code for drawing the Lissajous figure below - with velocity and acceleration vectors! - is just this.
The second screenshot shows a trajectory P(t) = (cos t, sin t), the parabola Q(t) = P(0) + t·P'(0) + t2/2·P''(0), and my favorite trick - the boxes - for drawing parabolas by hand. Its code is here.
9. Qdraw
Update: See my page on (My)Qdraw.
Qdraw is easy to extend. I generated the animation below
with these files:
(find-angg "MAXIMA/myqdraw3.mac") (find-angg "MAXIMA/topdf1.mac") (find-angg "MAXIMA/mkanim1.sh") (find-angg "MAXIMA/bezier2.mac") |
Click on the animation to enlarge it; click here to see it in flipbook format.
10. Debugging the Lisp (with Sly)
Update: I rewrote the instructions! The new version is here: (find-try-sly-intro).
Most people use Slime and Swank to debug the Lisp code of Maxima. I couldn't make Slime work with eepitch, so instead of Slime and Swank I'm using Sly, Slynk, and an eepitch-sly defined in this way, and I had to adapt these instructions. My code to use Sly and Slynk in Maxima is here: ~/.maxima/startsly.lisp.
See also this: eev-sly.html.
11. Maxima for students
This is a work in progress, and at this moment most of its docs are in Portuguese! If you don't understand Portuguese, the best starting points are these ones:
(find-windows-beginner-intro) http://anggtwu.net/2024-first-executable-notes.html http://anggtwu.net/2024-restructuring.html |
If you do understand Portuguese, then there's also this:
http://anggtwu.net/2024-convite-maxima.html http://anggtwu.net/2024-forumppg-1.html http://anggtwu.net/2024.1-C3.html |
I'm preparing a presentation for the EmacsConf 2024 about this - where "this" is how I made a bunch of students who had never seen a terminal in their lives install Emacs, eev, and Maxima. I had several really nice success cases and several very interesting failures - mainly from students who found very hard to ask questions.